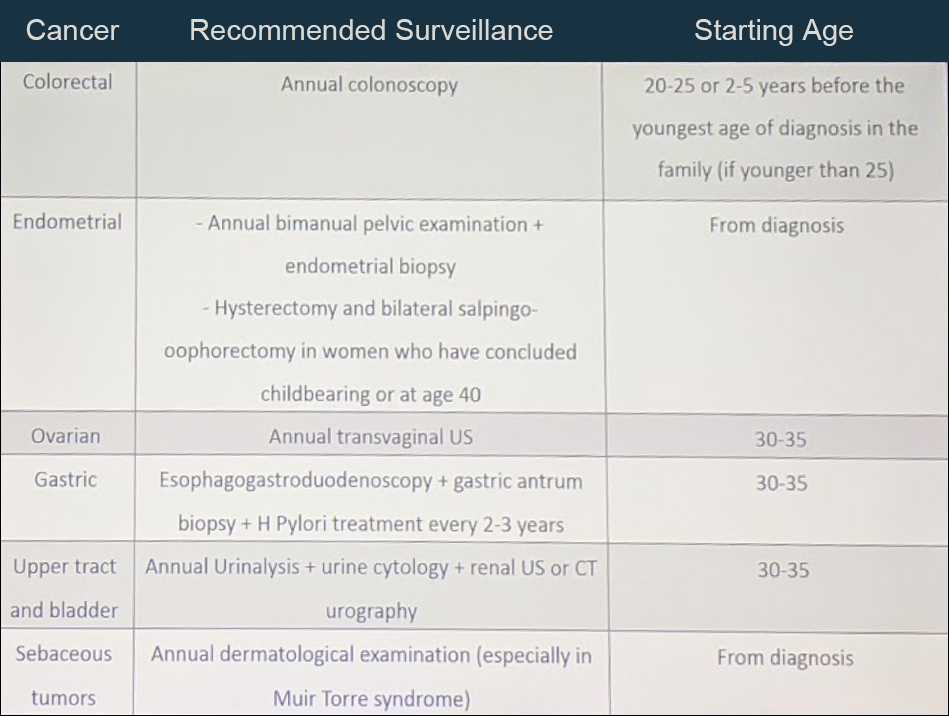
Bethesda Criteria Lynch Syndrome
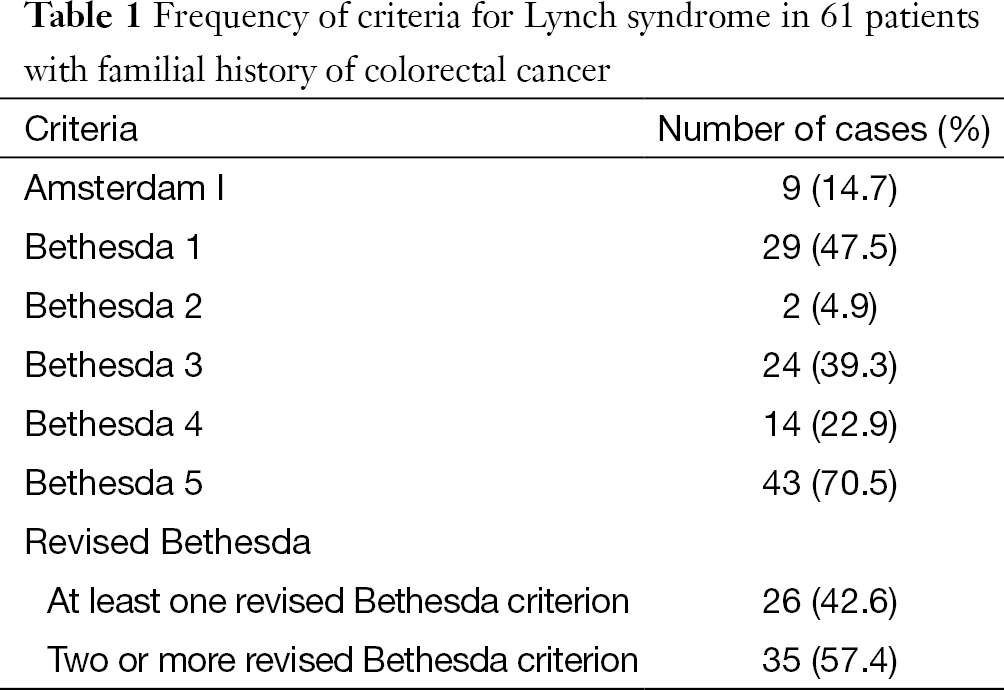
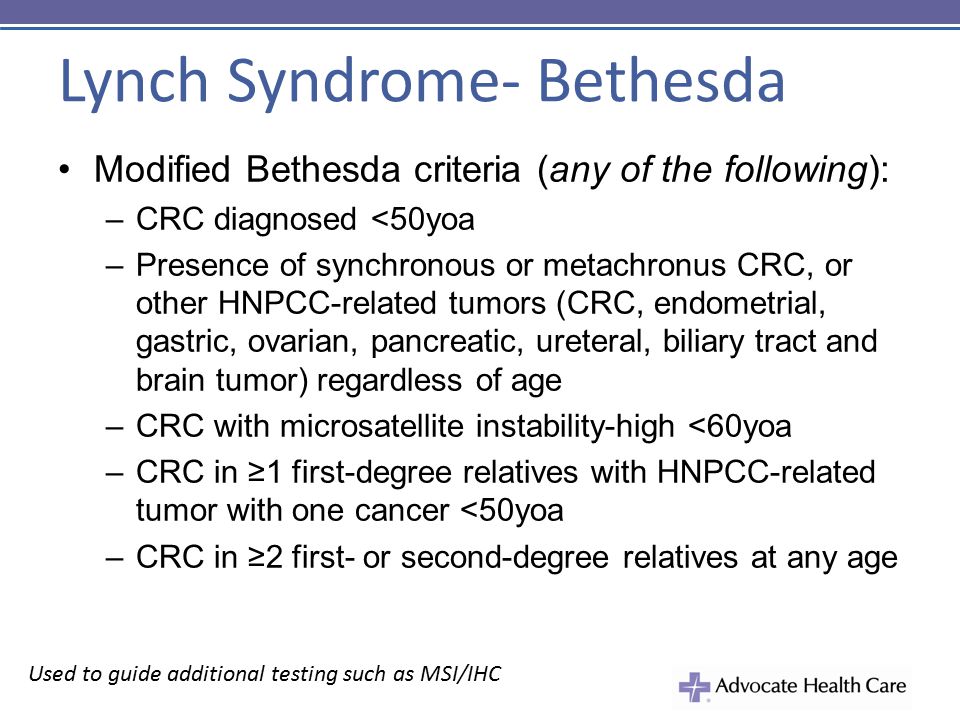
Bethesda criteria lynch syndrome. Et al J Natl Cancer Inst. Colorectal cancer with the MSI-H histology diagnosed in a patient. Lynch Syndrome Criteria Original or Modified Bethesda guidelines were met in 57 patients 114 not met in 189 397 whereas information was insufficient for definitive assessment in 244 489.
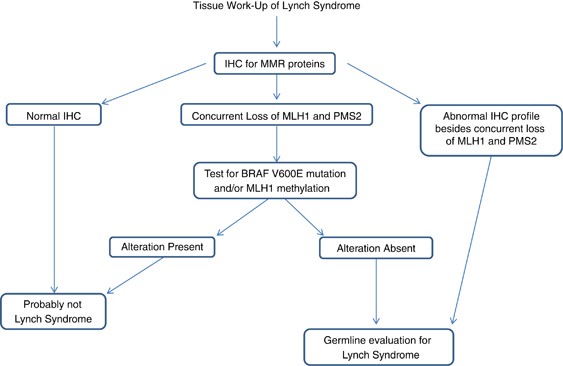
These barriers include limited family histories captured by health care providers and inconsistent reporting of MSI-H histology for colorectal cancer specimens by pathologists. Abstract Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC also known as Lynch syndrome is a common autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by early age at onset neoplastic lesions and microsatellite instability MSI. Colorectal or uterine cancer diagnosed in a patient how is less than 50 years of age.
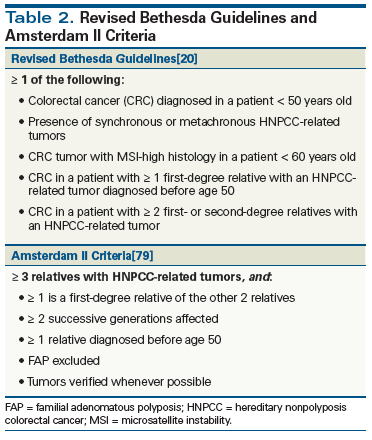
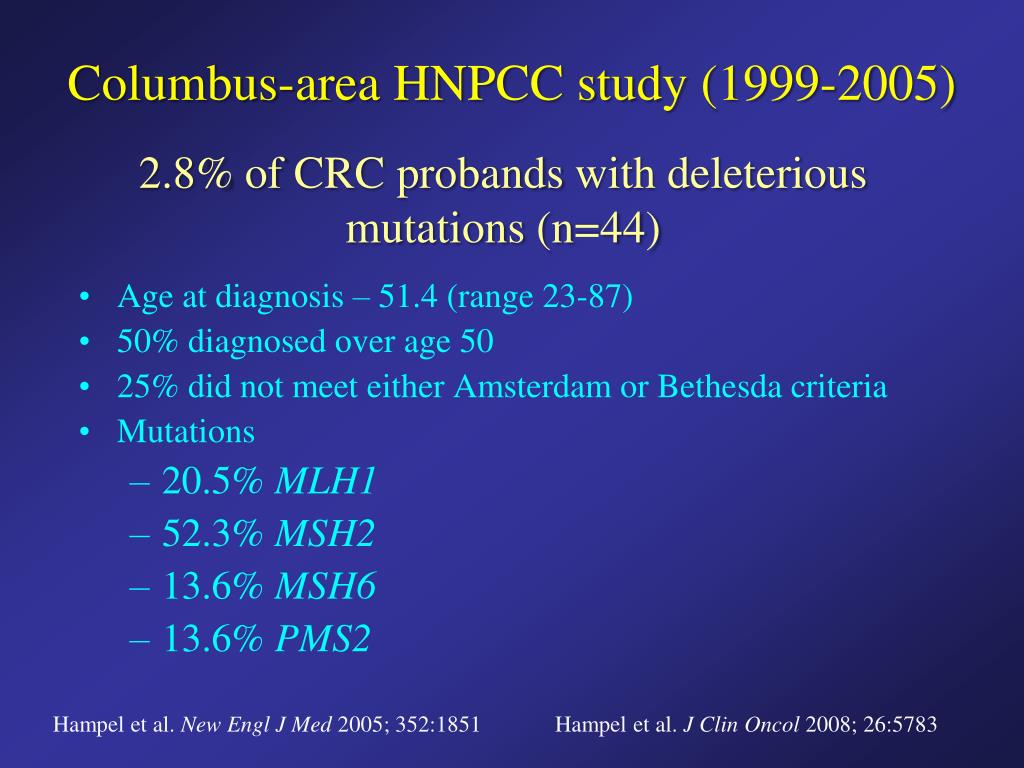
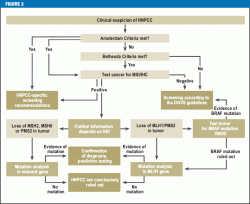
The Bethesda guidelines are more sensitive but less specific than the Amsterdam criteria. 3 or more family members with HNPCC related cancers one of whom is a first degree relative of the other two 2 successive affected generations. Lynch syndrome is the most common inherited CRC susceptibility syndrome and accounts for approximately 3 percent of newly diagnosed cases of CRC and 2 to 3 percent of endometrial cancer 1.
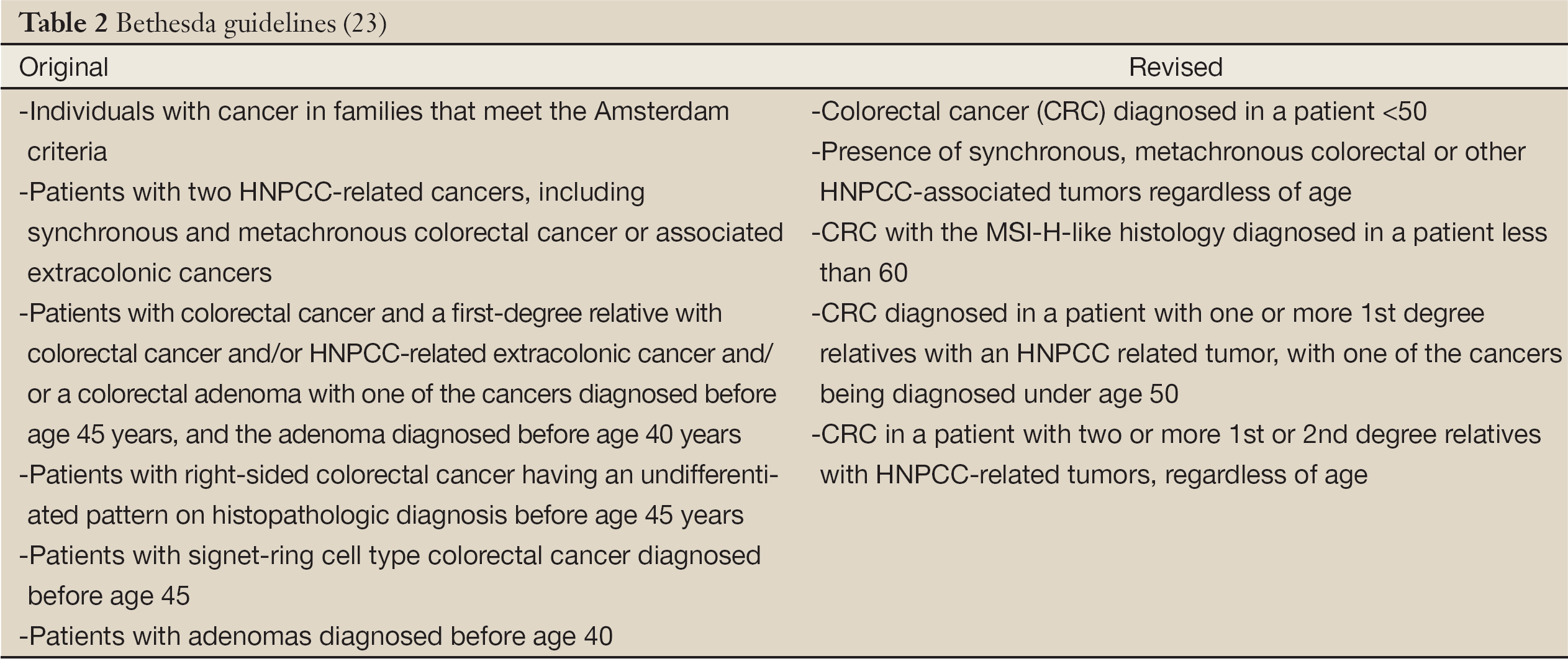
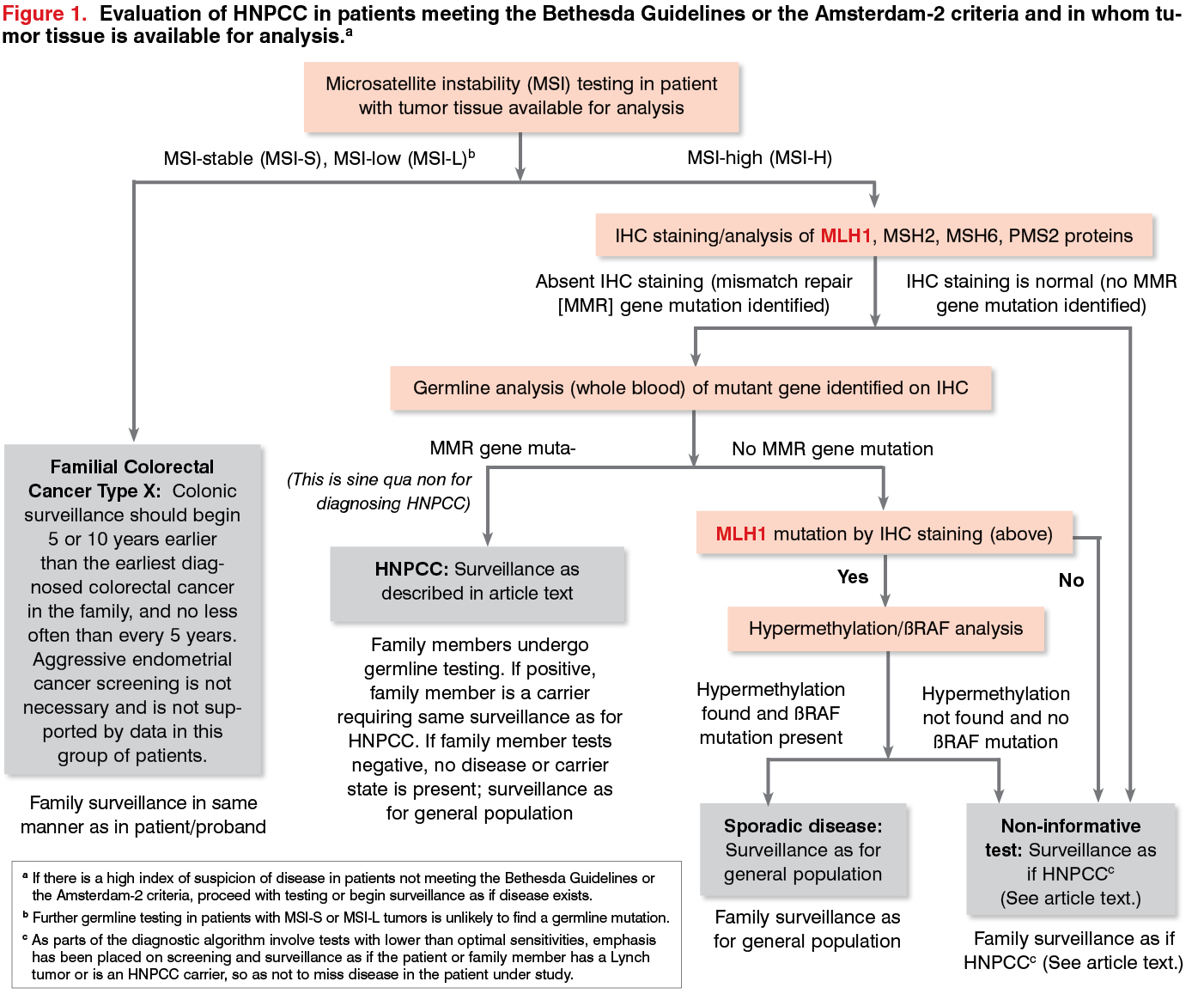
The NCCN 2020 recommends that testing for Lynch syndrome MLH1 MSH2 MSH6 PMS2 EPCAM sequence analysis includes individuals who meet the Bethesda guidelines the Amsterdam criteria who have a cancer diagnosis prior to age 50 or have a predicted risk for Lynch syndrome greater than 5 on one of the following prediction models. Diagnosis is based on either the Amsterdam criteria the Amsterdam criteria II or the Bethesda guidelines. Diagnostic criteria for Lynch syndrome Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC Revised Bethesda Diagnostic criteria Umar A.
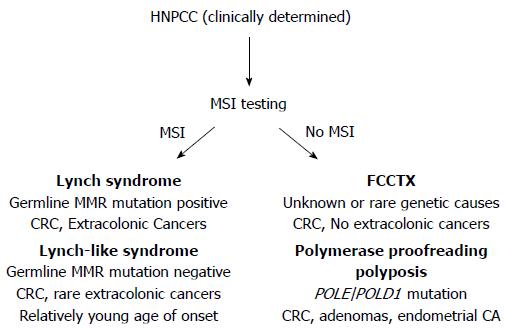
Lynch syndrome refers to individuals and families with a pathogenic germline mutation in one of the DNA mismatch repair genes MLH1 MSH2 MSH6 and PMS2 or the EPCAM gene. What are signs of Lynch syndrome. One relative should be a first-degree relative of the other two at least two successive generations should be affected at least one tumour should be diagnosed before the age of 50 years FAP should be excluded in the CRC case if any tumours should be verified by histopathological examination.
The more stringent Amsterdam criteria increase the chances of finding a germline mutation in either MSH2 or MLH1 from 25 to 86. Lynch syndrome is the cause of approximately 8 percent of incident CRC. It is estimated that 1 in 279 of the population carry mutations in DNA mismatch repair genes 2.
These are highly sensitive criteria so able to identify a large percentage of patients with the Lynch. Our study highlights several barriers in applying the revised Bethesda criteria to identify patients at risk for Lynch syndrome based on a diagnosis of an HNPCC tumor.
Below are the Revised Bethesda Guidelines for testing colorectal tumors for microsatellite instability MSI.
The latter group constituted patients with uncertain Bethesda guideline status. These are highly sensitive criteria so able to identify a large percentage of patients with the Lynch. Abstract Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC also known as Lynch syndrome is a common autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by early age at onset neoplastic lesions and microsatellite instability MSI. The Bethesda Criteria The Bethesda criteria were developed to identify colorectal cancer patients with possible Lynch syndrome HNPCC to be genetically studied and diagnosed. These barriers include limited family histories captured by health care providers and inconsistent reporting of MSI-H histology for colorectal cancer specimens by pathologists. What are signs of Lynch syndrome. The more stringent Amsterdam criteria increase the chances of finding a germline mutation in either MSH2 or MLH1 from 25 to 86. Lynch syndrome is the most common inherited CRC susceptibility syndrome and accounts for approximately 3 percent of newly diagnosed cases of CRC and 2 to 3 percent of endometrial cancer 1. Our study highlights several barriers in applying the revised Bethesda criteria to identify patients at risk for Lynch syndrome based on a diagnosis of an HNPCC tumor.
The Bethesda Criteria The Bethesda criteria were developed to identify colorectal cancer patients with possible Lynch syndrome HNPCC to be genetically studied and diagnosed. Diagnostic criteria for Lynch syndrome Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC Revised Bethesda Diagnostic criteria Umar A. Et al J Natl Cancer Inst. The more stringent Amsterdam criteria increase the chances of finding a germline mutation in either MSH2 or MLH1 from 25 to 86. These are highly sensitive criteria so able to identify a large percentage of patients with the Lynch. These barriers include limited family histories captured by health care providers and inconsistent reporting of MSI-H histology for colorectal cancer specimens by pathologists. Developing colorectal or endometrial cancer younger than age 50.




























Post a Comment for "Bethesda Criteria Lynch Syndrome"