Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule
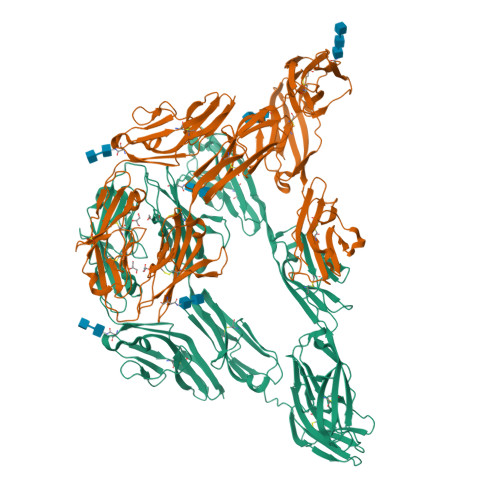
Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule. Mediates within retinal amacrine and ganglion cell subtypes both isoneuronal self-avoidance for creating an orderly dendritic arborization and heteroneuronal self-avoidance. DSCAM shows high structural homology to cellcell adhesion molecules such as BIG-1. Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule DSCAM is an HSA21 axon guidance molecule involved in the development of the nervous system 2.
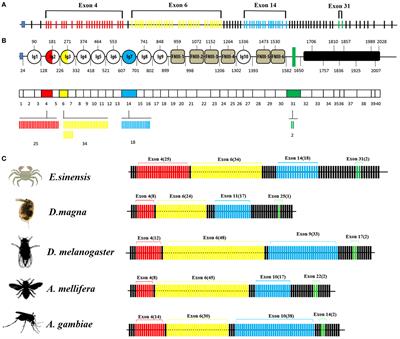
The Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule DSCAM is an Ig containing cell adhesion molecule with remarkable structural conservation throughout metazoansIn insects DSCAM has 38000 potential isoforms that convey axon guidance fasciculation and dendrite morphogenesis during neurodevelopment. DSCAM Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule 21q222 SYNJ1 synaptojanin 1 21q222 JAM2 junctional adhesion molecule 2 21q212 SIM2 single-minded homolog 2 Drosophila 21q22221q2213 ERG v-ets avian erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 21q223 PTTG1IP pituitary tumor-transforming 1 interacting protein 21q223. The neural cell adhesion molecule DSCAM Down syndrome.
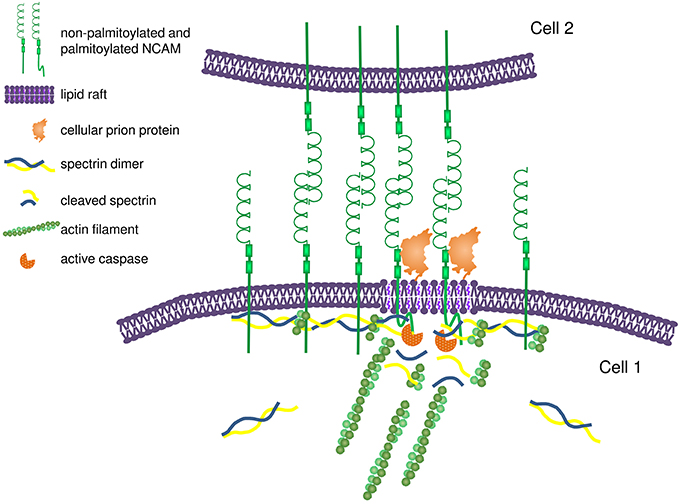
Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule and Neural Wiring. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule interacts with PRKAG1 subunit and plays an important role in netrin-1 induced neurite outgrowth. From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like 1 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the DSCAML1 gene.
DSCAM was found to be expressed largely in the developing nervous system. Promotes repulsion between specific neuronal processes of either the same cell or the same subtype of cells. Yamakawa et al.
In vertebrates DSCAM is expressed throughout the nervous system and seems. Down Syndrome DS Cell Adhesion Molecules DSCAMs are transmembrane proteins of the immunoglobulin superfamily. 1998 isolated and characterized a novel gene DSCAM Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule which was found by homology searches to be a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that represents a new class of neural cell adhesion molecules.
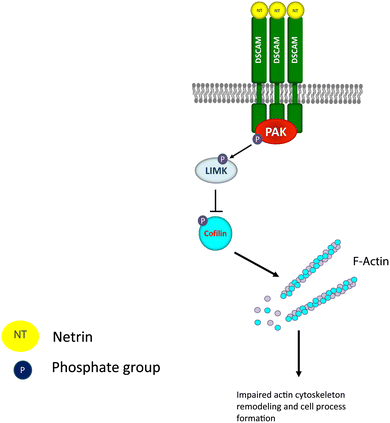
Knockdown of DSCAM inhibits netrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of UNC5C and Fyn as well as the interaction of UNC5C with Fyn. Elav thus co-regulates APA and alternative splicing to generate specific Dscam1. Down Syndrome DS is a major cause of mental retardation and is associated with characteristic well-defined although subtle brain abnormalities many of which arise after birth with particular.
Alternatively spliced down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam controls innate immunity in crab Alternatively-spliced hypervariable immunoglobulin domain-encoding molecules called Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam have been widely detected as components of the arthropod immune system. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam in invertebrates and DSCAM in vertebrates is a transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily that exists in a wide range of animals.
All Dscam and DSCAM molecules share similar.
Dscam1 Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule 1 fruit fly Dscam1 establishes the columnar units through lineage-dependent repulsion between sister neurons in the fly brain. In vertebrates DSCAM is expressed throughout the nervous system and seems. In murine models of DS the DSCAM. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule DSCAM associates with uncoordinated-5C UNC5C in netrin-1-mediated growth cone collapse. The neural cell adhesion molecule DSCAM Down syndrome. DSCAM shows high structural homology to cellcell adhesion molecules such as BIG-1. Elav thus co-regulates APA and alternative splicing to generate specific Dscam1. Knockdown of DSCAM inhibits netrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of UNC5C and Fyn as well as the interaction of UNC5C with Fyn. Mediates within retinal amacrine and ganglion cell subtypes both isoneuronal self-avoidance for creating an orderly dendritic arborization and heteroneuronal self-avoidance.
Alternatively spliced down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam controls innate immunity in crab Alternatively-spliced hypervariable immunoglobulin domain-encoding molecules called Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam have been widely detected as components of the arthropod immune system. Human DSCAM is located within the DS critical region of chromosome 21 duplicated in Down Syndrome patients and mutations or copy-number variations of this gene have also been associated to Fragile X syndrome intellectual disability autism and bipolar disorder. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule Dscam in invertebrates and DSCAM in vertebrates is a transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily that exists in a wide range of animals. 1998 isolated and characterized a novel gene DSCAM Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule which was found by homology searches to be a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that represents a new class of neural cell adhesion molecules. 15 - 17 Down syndrome is the result of triplication for human chromosome 21 which causes an overexpression of the thousands of genes located there. Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule and Neural Wiring. DSCAM was found to be expressed largely in the developing nervous system.


































Post a Comment for "Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule"