Scalene Block For Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Scalene block for thoracic outlet syndrome. We performed a retrospective study to determine if relief of pain was related to brachial plexus blockade in these patients. There is no gold standard for diagnosing thoracic outlet compression syndrome TOS however anesthetic blocks of the anterior scalene muscle ASM have been used as a means of predicting which patients may benefit from surgical decompression. ScalenePectoralis Muscle Blocks Injection of a local anesthetic into the anterior scalene muscle ASM andor pectoralis minor muscle PM was introduced more than 10 years ago by Dr.
We performed a retrospective study to determine if relief of pain was related to brachial plexus blockade in these patients. This animation illustrates how physicians at the Johns. Scalene muscle injections are used to confirm the diagnosis of neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome and predict the response of patients to surgery.
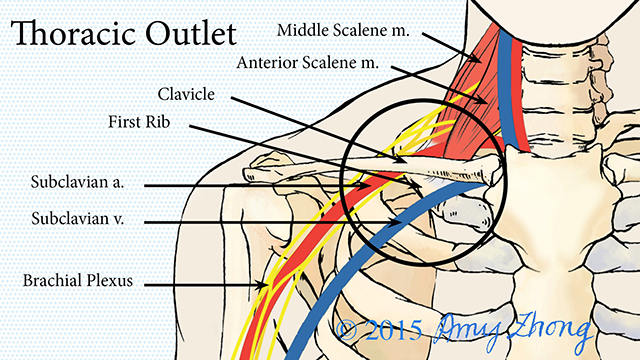
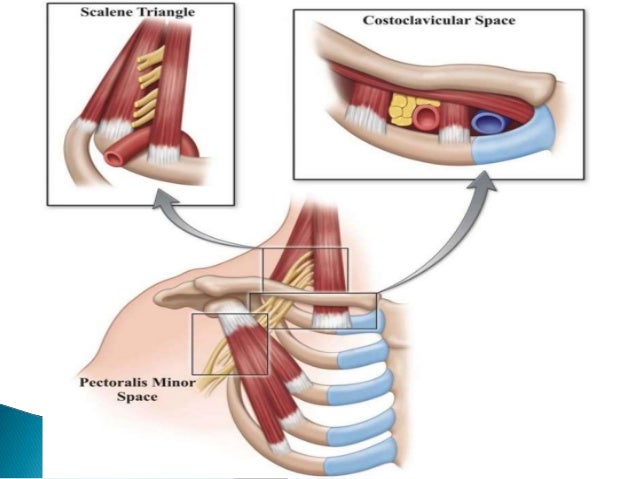
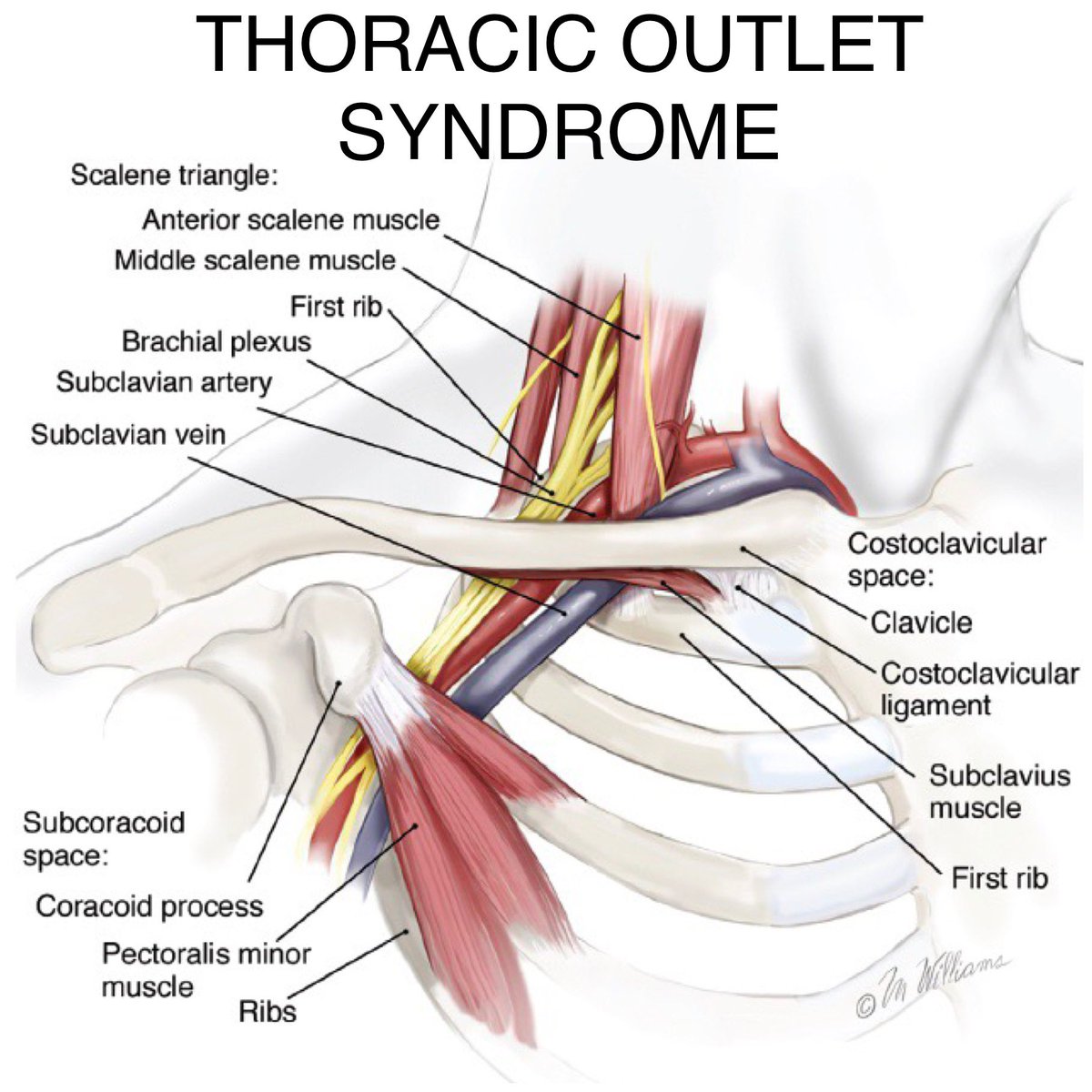
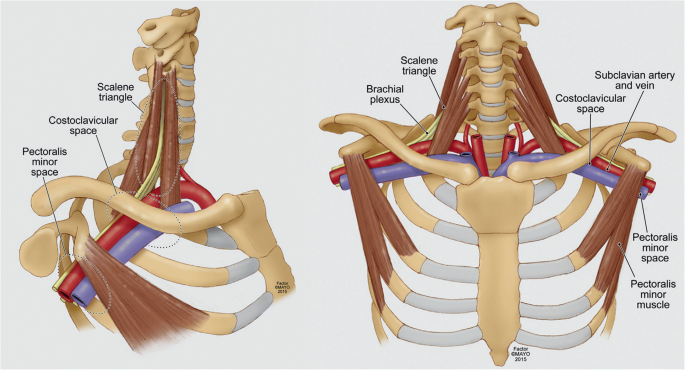
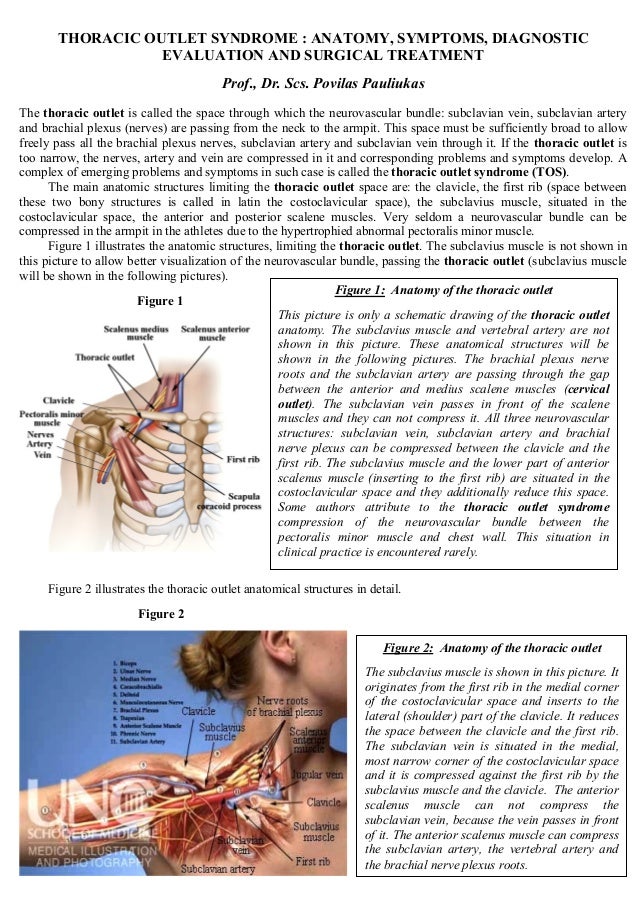
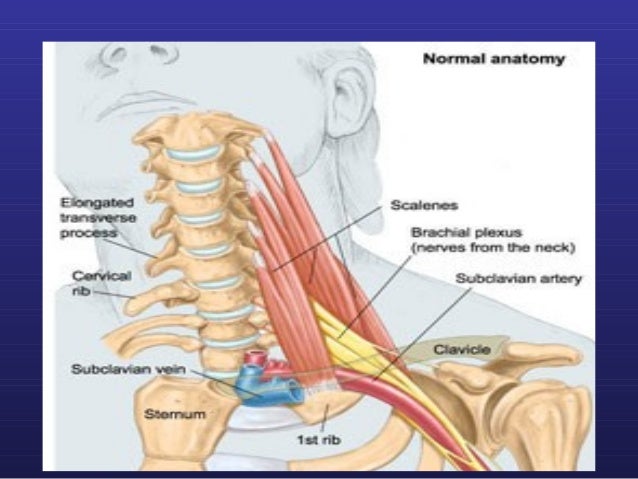
Scalene muscle injections are used to confirm the diagnosis of neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome and predict the response of patients to surgery. Scalene Blocks and Their Role in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome TOS is a constellation of symptoms caused by compression of neurovascular structures as they traverse the superior thoracic outlet.
Compression may be due to one or more of the following factors. Anesthetic block of the anterior scalene muscles has become a dual-purpose procedure providing diagnostic confirmation of TOS and as a reliable indicator of which patients may respond favorably to surgery. Thoracic outlet syndrome is a neurovascular disorder resulting from compression of the brachial plexus andor subclavian vessels in the interval between the neck and axilla.
An anterior scalene muscle ASM block entails injection of an anesthetic such as lidocaine into the scalene muscles. The block is thought to work through both analgesic and muscle relaxation effects but evidence of the latter is lacking. To measure changes in upper limb work and power capacity before and after anterior scalene muscle block ASMB to suggest thoracic outlet syndrome caused by costoclavicular space compression.
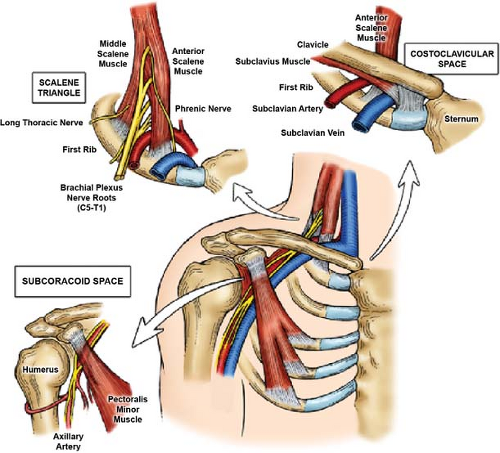
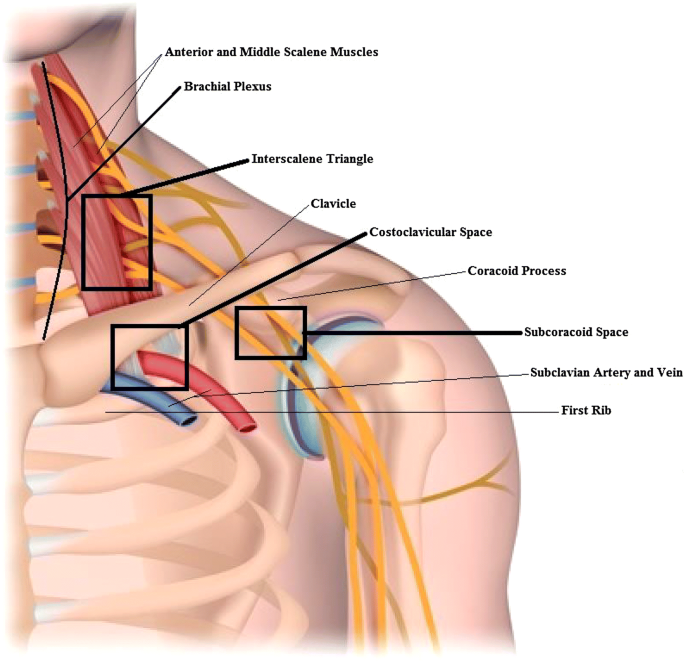
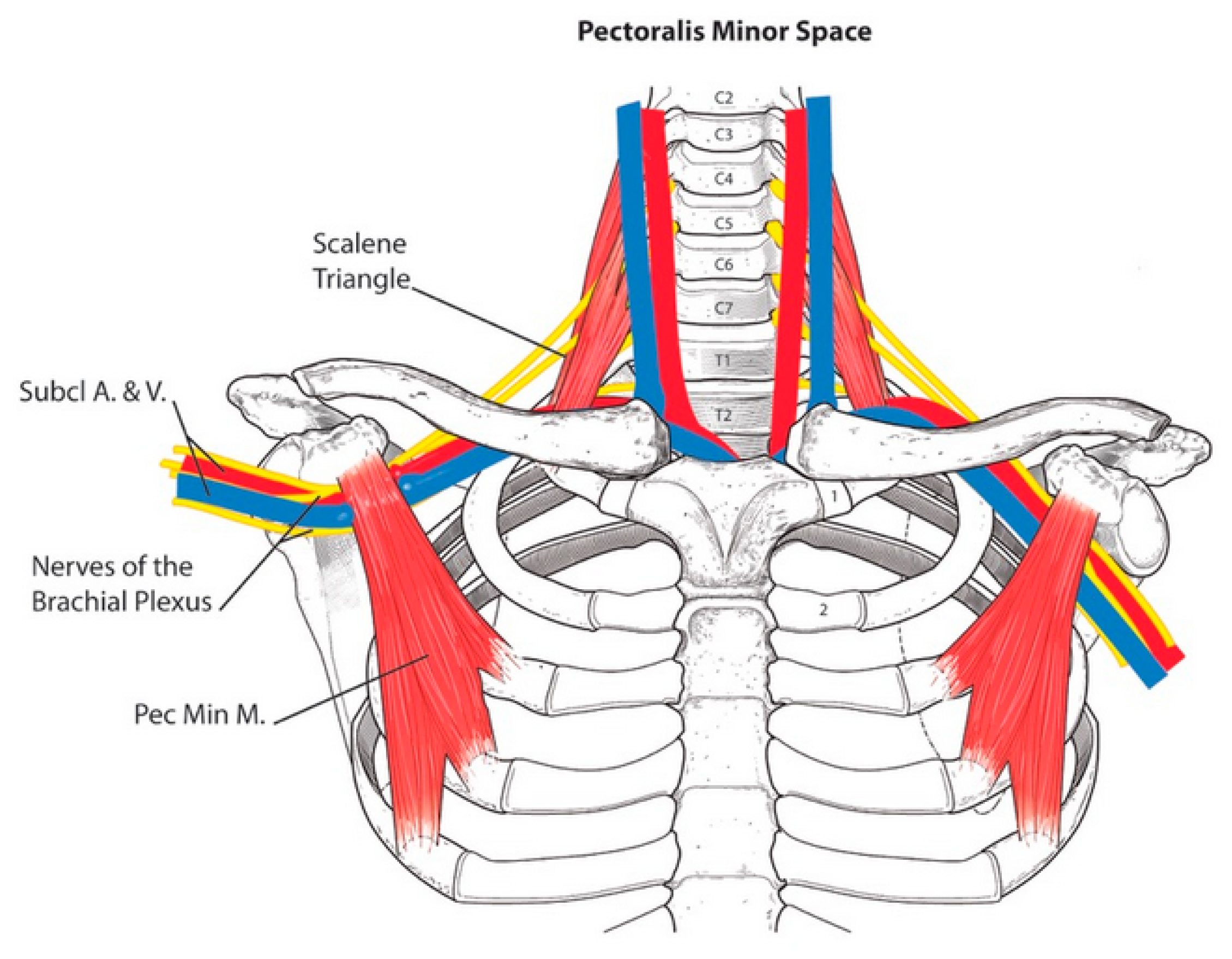
Neurogenic TOS is most frequently characterized by compression of the brachial plexus nerve roots C5 to T1 within the scalene triangle. Ann Vasc Surg 1998. To measure changes in upper limb work and power capacity before and after anterior scalene muscle block ASMB to suggest thoracic outlet syndrome caused by costoclavicular space compression.
Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome TOS From 85-95 of all patients with TOS are affected by neurogenic TOS. We evaluated 34 patients disabled by symptoms suggesting thoracic outlet syndrome.
Sheldon Jordan UCLA as a means to improve the diagnosis of neurogenic TOS and to help predict outcomes of treatment.
To measure changes in upper limb work and power capacity before and after anterior scalene muscle block ASMB to suggest thoracic outlet syndrome caused by costoclavicular space compression. 1-2 of the population. The block is thought to work through both analgesic and muscle relaxation effects but evidence of the latter is lacking. Thoracic outlet syndrome disorder can sometimes be diagnosed in a physical exam by tenderness in the supraclavicular area weakness andor a pins and needles feeling when elevating the hands weakness in the fifth little finger and paleness in the palm of one or both hands when the individual. This animation illustrates how physicians at the Johns. We performed a retrospective study to determine if relief of pain was related to brachial plexus blockade in these patients. Thoracic outlet syndrome is a neurovascular disorder resulting from compression of the brachial plexus andor subclavian vessels in the interval between the neck and axilla. Sheldon Jordan UCLA as a means to improve the diagnosis of neurogenic TOS and to help predict outcomes of treatment. Compression may be due to one or more of the following factors.
Over a two-year period a series of patients. An anterior scalene muscle ASM block entails injection of an anesthetic such as lidocaine into the scalene muscles. We performed a retrospective study to determine if relief of pain was related to brachial plexus blockade in these patients. Scalene muscle injections are used to confirm the diagnosis of neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome and predict the response of patients to surgery. Compression may be due to one or more of the following factors. Mechanism and Causes of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. To measure changes in upper limb work and power capacity before and after anterior scalene muscle block ASMB to suggest thoracic outlet syndrome caused by costoclavicular space compression.































Post a Comment for "Scalene Block For Thoracic Outlet Syndrome"