Pkd Disease Life Expectancy
Pkd disease life expectancy. Without treatment Kidney Failure patients may die within weeks. Some patients can live their entire life without developing into the end stages of the disease. Risk factors for kidney decline include having a change in the PKD1 gene younger age of onset of the disorder increased kidney size and hypertension.
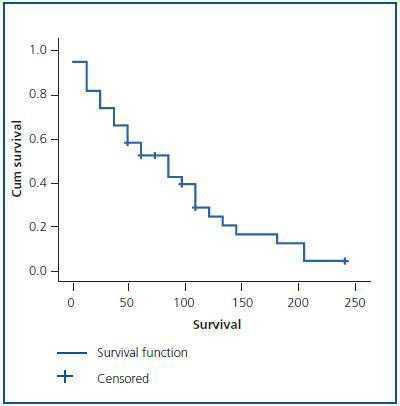
The rate of progression of kidney decline varies greatly. Patients who develop renal failure early in their lives will have more complications and a shorter life span. In general patients with PKD will not experience any symptoms until they are over 30 to 40 years.
Men and boys are at a greater risk of progressive kidney disease as well. Generally speaking life expectancy of PKD patients is directly linked to how fast the kidney functions decline. It causes abnormal kidney development in.
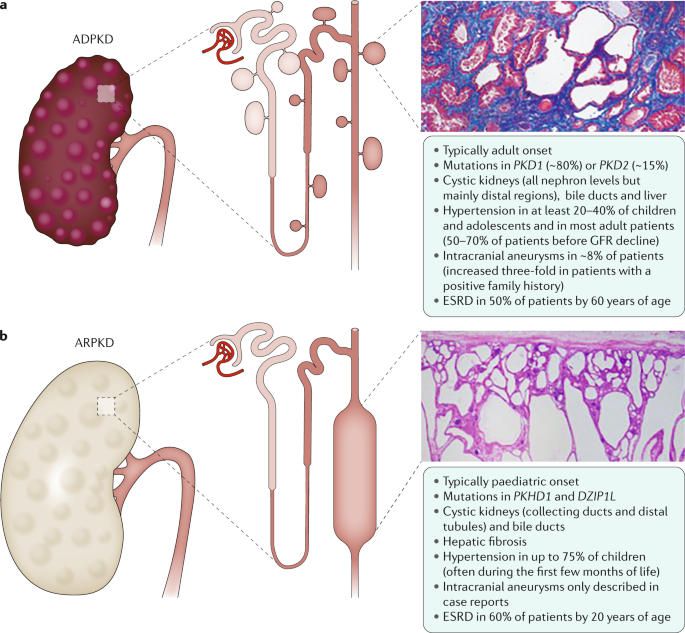
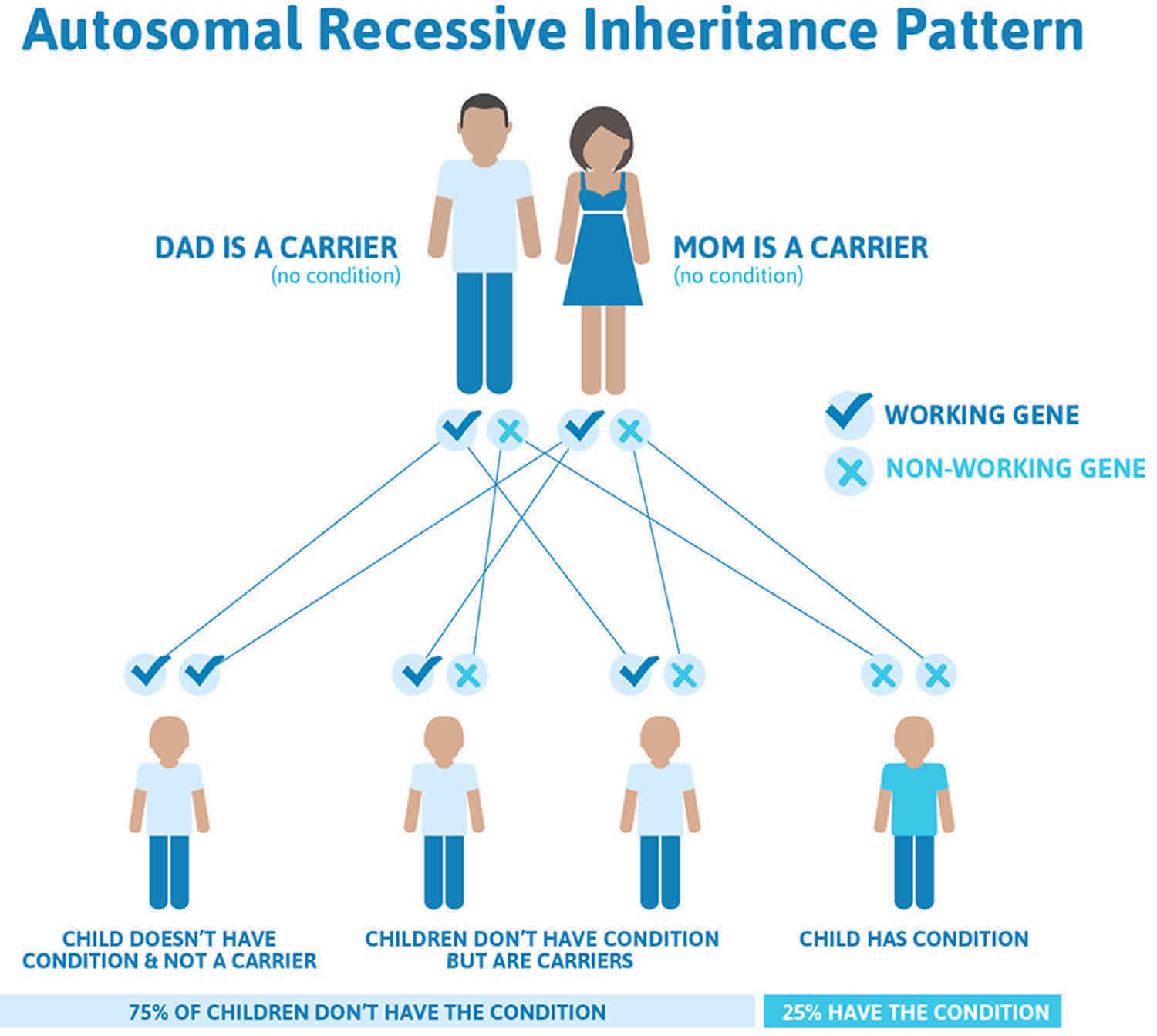
Its difficult to predict exactly how long a child with ARPKD will live because theres very little data showing long-term survival rates. Some people retain adequate kidney function until very late in life. Autosomal recessive PKD is sometimes called infantile PKD.
About 8 or 9 out of 10 babies with ARPKD who survive the first month of life will live until theyre at least 5 years old. Trends in life expectancy. Your life expectancy and outlook with ADPKD depend on several factors including.
ARPKD is a rare form of PKD also called infantile PKD. The age at which symptoms begin to occur varies with individuals but is usually around 50 years old. Signs begin in the early months of life or even while the baby is still developing in the uterus womb.
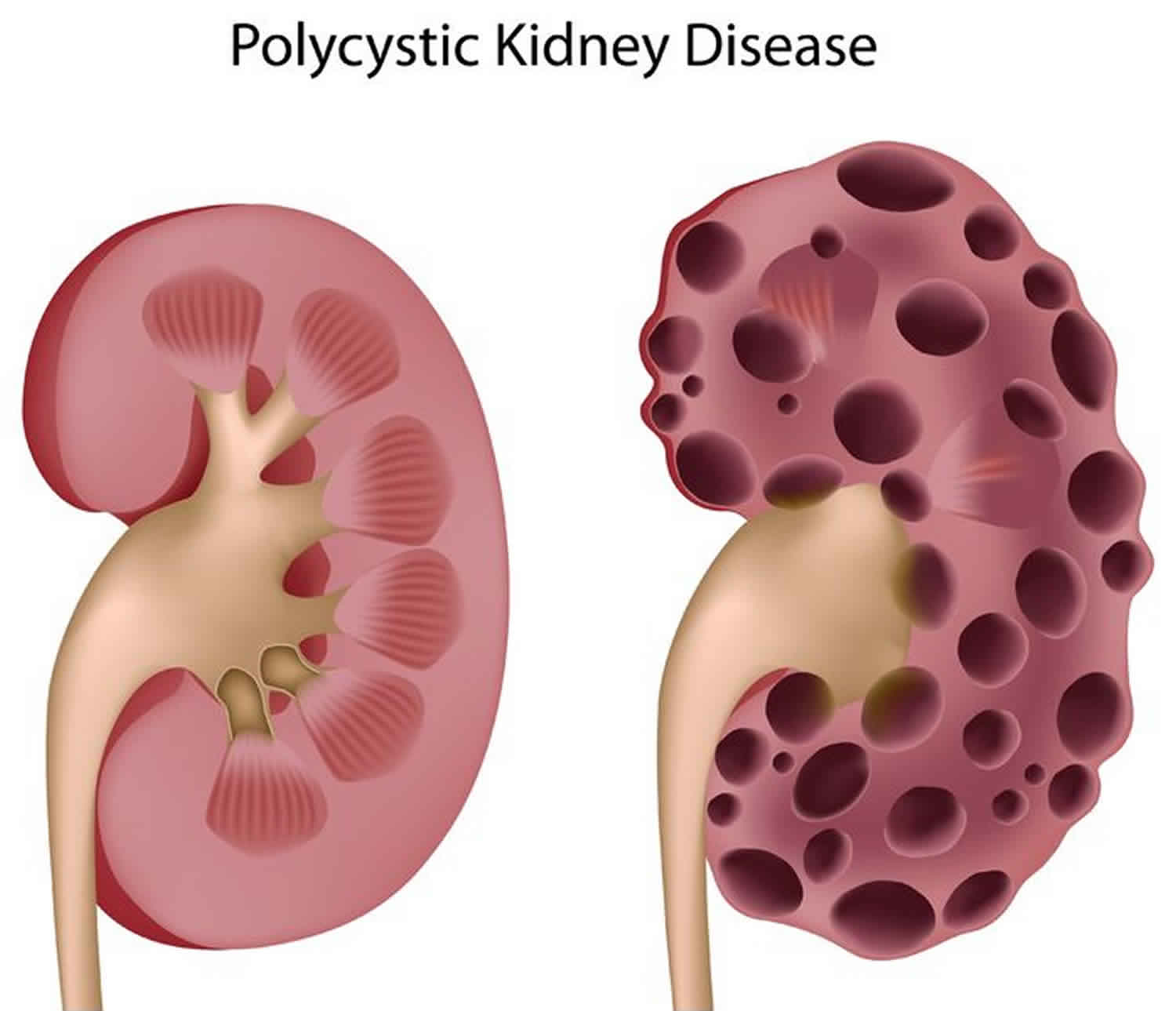
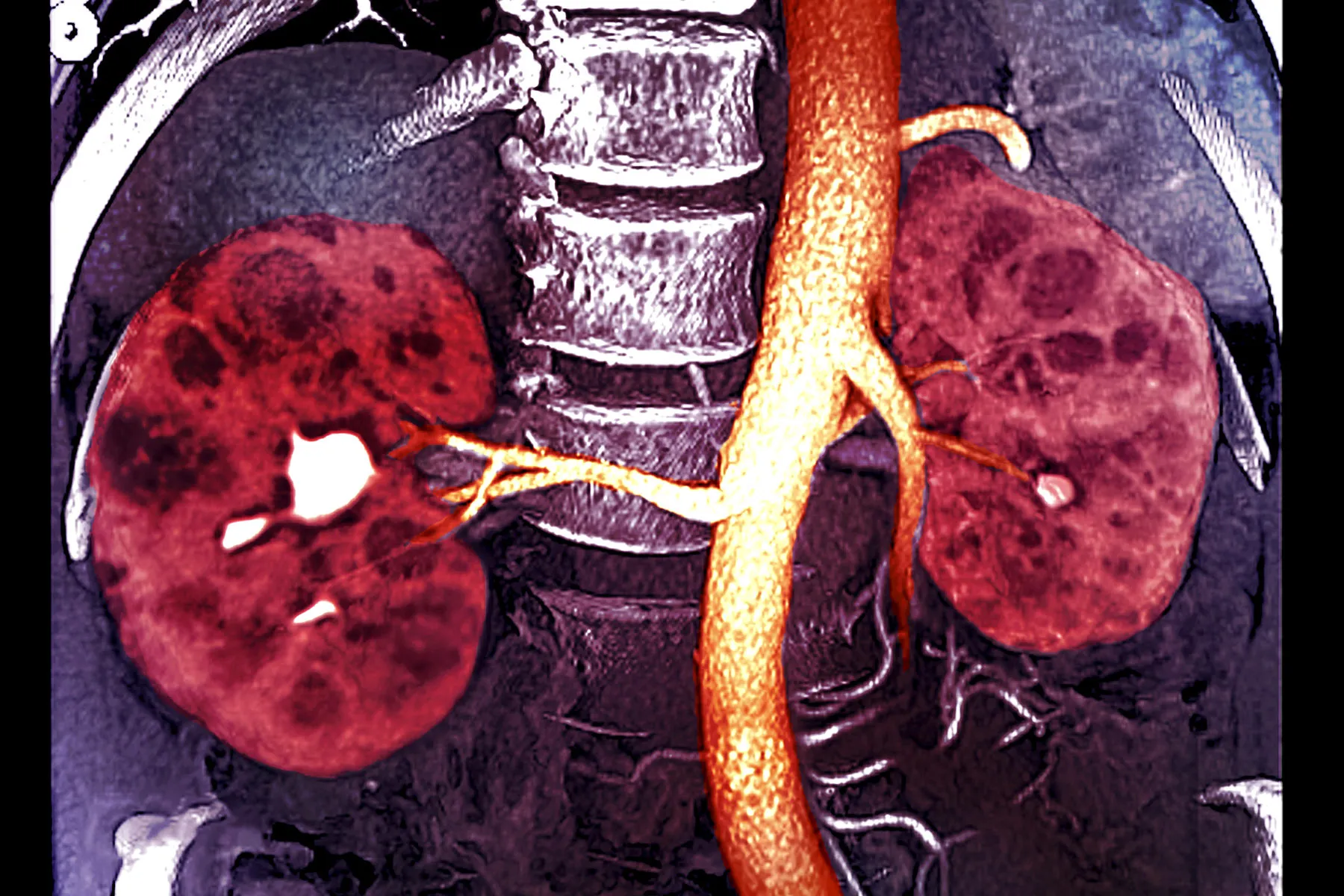
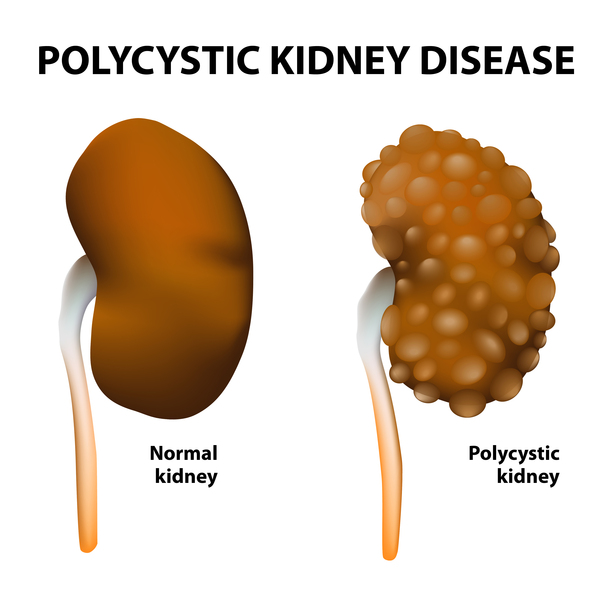
What Is the Life Expectancy for Polycystic Kidney Disease. Life expectancy with PKD differs significantly from individual to individual.
Life expectancy depends on the severity and the progression of the disease to end-stage renal disease ESRD.
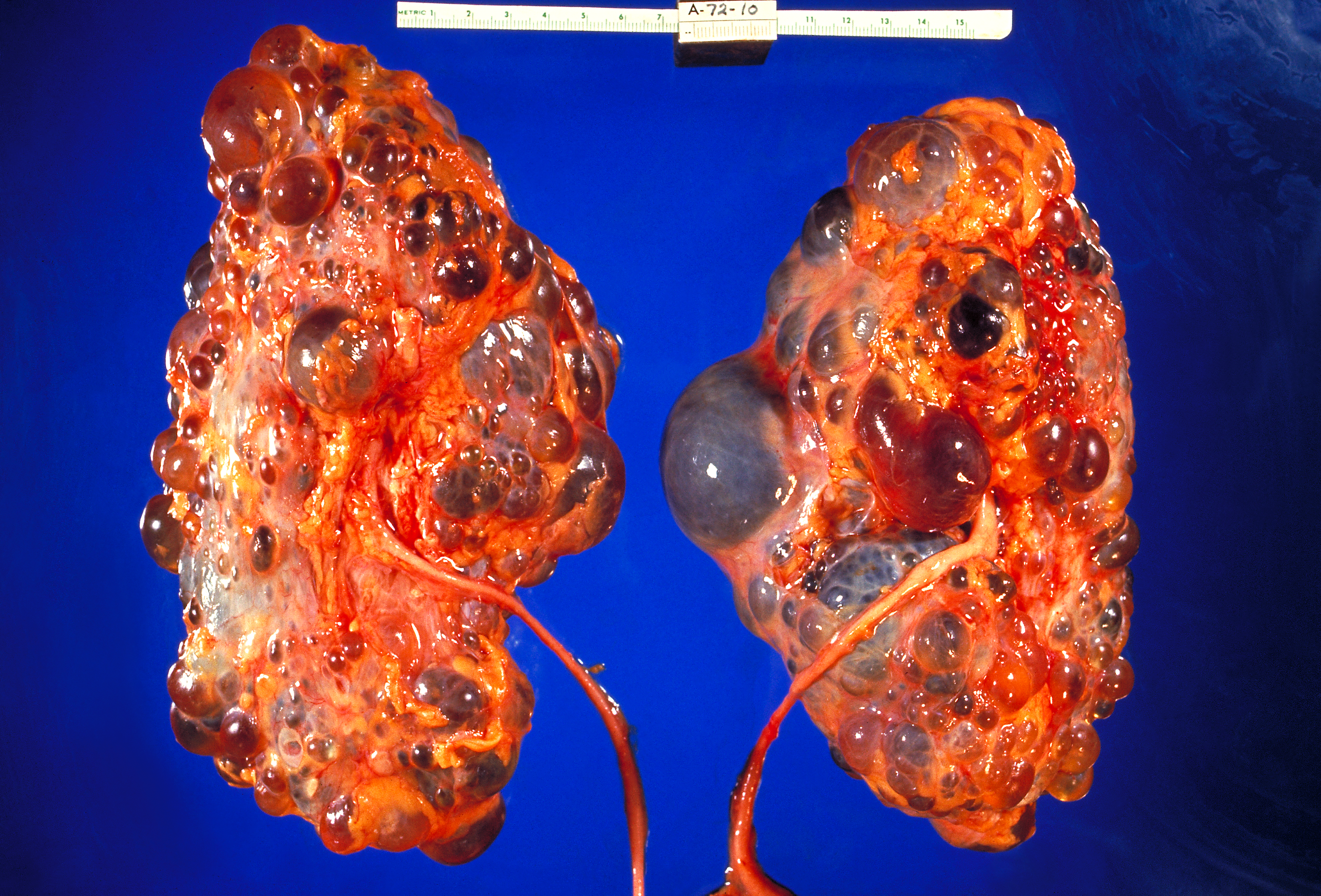
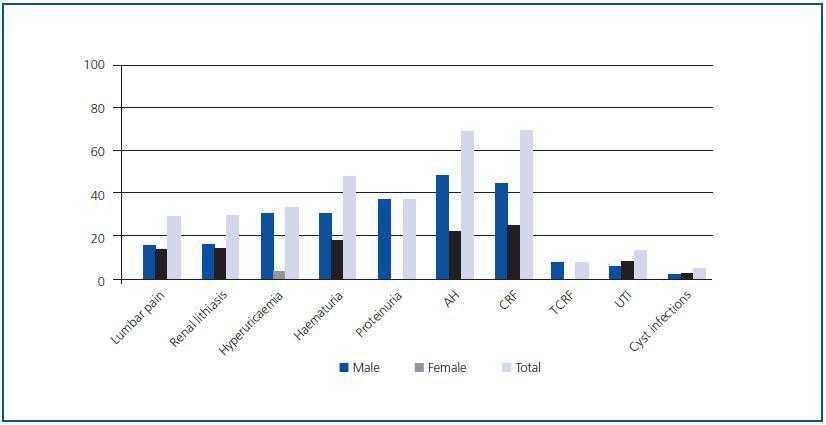
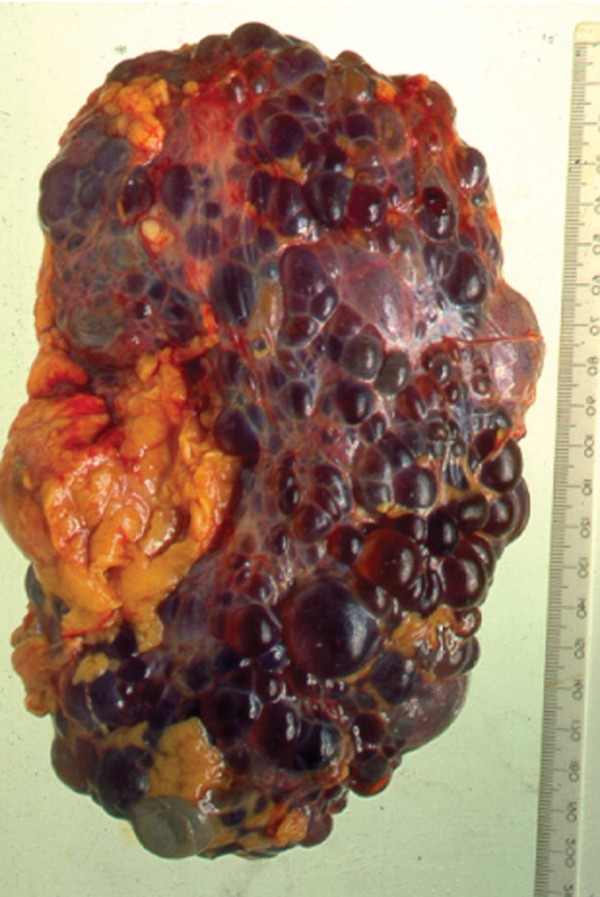
Life expectancy depends on the severity and the progression of the disease to end-stage renal disease ESRD. Here are the facts about polycystic liver disease you need to better understand the condition. In general patients with PKD will not experience any symptoms until they are over 30 to 40 years. Its difficult to predict exactly how long a child with ARPKD will live because theres very little data showing long-term survival rates. Oral contraceptives and estrogen replacement therapy are also associated with more severe disease 23-25. Cysts can begin to grow at any age but are rare in childhood and more common with age. This form of ARPKD is extremely rare. Men and boys are at a greater risk of progressive kidney disease as well. ARPKD is a rare form of PKD also called infantile PKD.
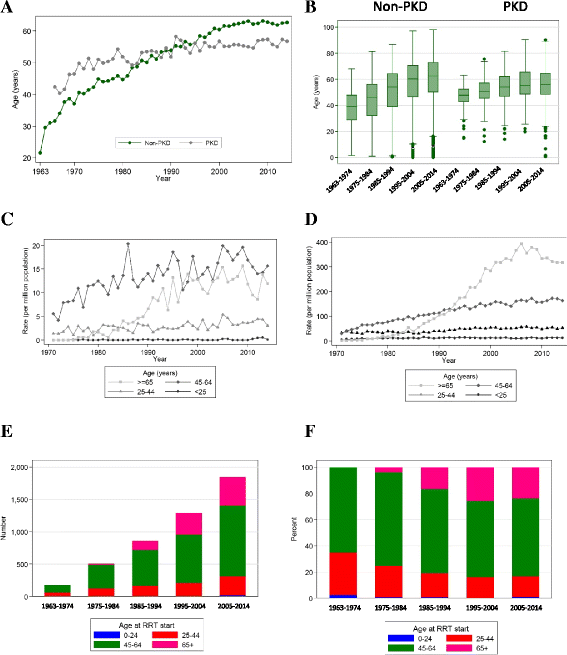
At this point information on kidney disease caused by GANAB mutations is limited but it appears to be milder than PKD1. The average age of end-stage kidney disease that is needing dialysis or a transplant is approximately 55 years in PKD1 versus 74 years in PKD2 patients. Risk factors for kidney decline include having a change in the PKD1 gene younger age of onset of the disorder increased kidney size and hypertension. Kidney failure occurs at an earlier age in PKD1 patients. It tends to be very serious progresses rapidly and is often fatal in the first few months of life. Some people retain adequate kidney function until very late in life. About 8 or 9 out of 10 babies with ARPKD who survive the first month of life will live until theyre at least 5 years old.

































Post a Comment for "Pkd Disease Life Expectancy"